Appointment Contact
+91 9137218557145B Lilian Hs, Sh 6, 1st Flr, Bhandar Galli,
Mahim West, Mumbai – 400016.10:00 am - 01:00 pm | 4:00 pm - 8:00 pm
drnikhilgurjar@gmail.com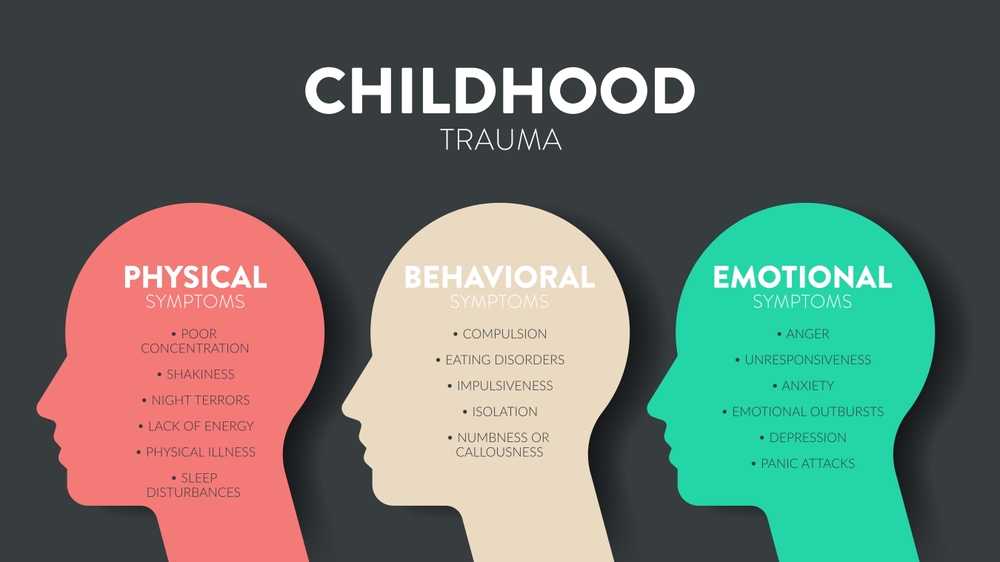
Impact of childhood trauma
Although childhood is frequently associated with innocence and pleasant days, it can also be a time of trauma and misfortune for many people. Whether it results from bereavement, abuse, neglect, or other upsetting events, childhood trauma can have a significant and long-lasting effect on a person's life. This blog examines the numerous ways that childhood trauma can impact one's physical, mental, and emotional well-being and emphasizes the value of healing and early intervention.
Comprehending Childhood Trauma
Any substantial upsetting event or sequence of events that occur throughout childhood and exceed a child's capacity for coping are referred to as childhood trauma. This can include neglect, witnessing domestic violence, parental substance misuse, physical, emotional, or sexual abuse, or experiencing a serious illness. These encounters have the potential to leave a lasting psychological impact on children, affecting their growth and worldview.
The Effects of Childhood Trauma on Psychology
Emotional Dysregulation: Children who have traumatic experiences frequently have trouble controlling their emotions. They might react to commonplace events with strong and erratic emotions like fear, grief, or rage. Adults may still struggle with this dysregulation, which can make it challenging to control relationships and emotions.
Development of Mental Health Disorders: Adversity during childhood poses a serious risk for the emergence of a number of mental health conditions in later life. Early traumatic events are frequently associated with conditions like melancholy, anxiety, borderline personality disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Unresolved trauma might show up as chronic anxiety or enduring emotions of helplessness or unworthiness.
Effect on Cognitive Functioning: Trauma can also have an impact on cognitive development, which can result in issues with learning, memory, and focus. Children who have experienced trauma may find it difficult to concentrate in class or to remember what they have learned. This may lower their self-esteem and present long-term difficulties in their academic and professional lives.
Interpersonal Relationships: People's ability to establish and sustain relationships is frequently affected by trauma. Those who have gone through childhood trauma frequently struggle with trust issues, interpersonal concerns, and fear of abandonment. These obstacles may make it challenging to establish wholesome, sustaining connections, which may result in social exclusion or unhealthy patterns of interactions.
Chronic Health Conditions and the Physical Effects of Childhood Trauma: Studies have indicated that childhood trauma may play a role in the development of chronic health conditions later in life. People who endured severe trauma as children are more likely to suffer from heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and chronic discomfort. These health problems are exacerbated by the protracted stress response that trauma causes, which can result in inflammation and a compromised immune system.
Substance Abuse and dangerous Behaviors: Those who have gone through traumatic experiences as children are more likely to abuse substances and engage in other dangerous behaviors. As coping methods, drug and alcohol abuse can be used to dull the agony of unresolved trauma. Addiction and additional physical health issues may result from this
Effects on the Nervous System: Trauma can alter the brain and nervous system permanently. The body's perpetual state of hyperarousal, or being on high alert, can cause heart palpitations, insomnia, and an accelerated startle response. Chronic stress can eventually have a negative impact on one's physical health, increasing the risk of diseases including hypertension and digestive problems.
Early Intervention and Healing Are Critical
Early intervention and rehabilitation are critical because of the tremendous effects that childhood trauma can have. Early trauma treatment can stop more serious mental and physical health problems from arising later in life.
Support for Therapy: Counseling can be a very useful tool for people trying to process and recover from traumatic experiences as children. Treatments for trauma that have been demonstrated to be successful include eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), trauma-focused therapy, and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). Individuals can strengthen their resilience, create healthier coping strategies, and reframe their experiences with the aid of therapy.
Creating a Support Network: The emotional support required to recover from trauma can be obtained through a robust network of friends, family, or support organizations. People can feel less alone and more empowered in their healing process when they perceive people to be understanding and supportive of them.
Self-Care and Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness and self-care on a regular basis can help promote recovery. Engaging in practices like journaling, exercise, meditation, and healthy eating can aid people with stress management, mental health, and reestablishing a connection with their physical selves.
Education and Awareness: Preventing and treating childhood trauma requires increasing public knowledge of its effects. The effects of trauma can be lessened and recovery can be encouraged by teaching parents, caregivers, and educators about the warning signs of trauma and the value of providing safe, supportive environments for kids.
In summary
A person's physical, mental, and emotional well-being, as well as other areas of their life, can all be negatively impacted by childhood trauma. However, it is possible to overcome the difficulties caused by trauma if early intervention, therapy support, and a healing-focused approach are taken. Through comprehending the consequences of childhood trauma and implementing measures to mitigate it, we can assist people in leading more robust and satisfying lives.


